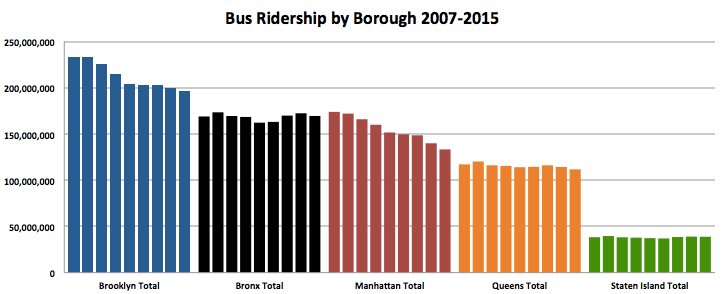
Bus ridership in New York City fell 16 percent between 2002 and 2015 -- a troubling trend that only gained steam last year. A look at the changes in each borough by transportation analyst Eric Goldwyn shows that since 2007, the bus ridership decline has been concentrated in Manhattan and Brooklyn.
Between 2007 and 2015, bus ridership in the Bronx, Queens, and Staten Island plateaued while dropping substantially in the other two boroughs. (This pattern in Manhattan and Brooklyn extends at least as far back as 2005.)
Another look at ridership by borough 2007-2015. Thanks @trnsprtst for the tip. I also added the raw data for those who are interested. pic.twitter.com/OA3HAxJnEB
— eric goldwyn (@ericgoldwyn) February 20, 2017
The reasons for the discrepancy aren't clear. Service cuts in 2010 may have disproportionately affected these two boroughs, and some speculation on Twitter points to demographic change (younger people ride the bus less than older people.)
But one factor is almost certainly traffic congestion. Average vehicle speeds in Manhattan below 60th Street declined 12 percent from 2010 to 2015, according to DOT. Without an effective traffic reduction plan from Mayor de Blasio or action from Governor Cuomo to enact toll reform, the traffic that makes buses so slow and unreliable may only get worse.
Of course, while the center city may have the worst traffic, bus service all over the five boroughs gets slowed down on congested streets, as you can see in this map of p.m. bus speeds from DOT's recent Mobility Report [PDF]. Systemwide strategies to help buses beat traffic can reverse the decline in Manhattan and Brooklyn and grow bus ridership again in the Bronx, Queens, and Staten Island.