Wondering how the MTA could afford to restore service on 24 bus lines and postpone next year's fare hikes? New budget documents show where the transit system's revenues and costs beat expectations, leaving the small and fragile surplus. The biggest savings came from cheap energy. Revenues from riders were up, but the important yet volatile real estate transaction tax came in under expectations.
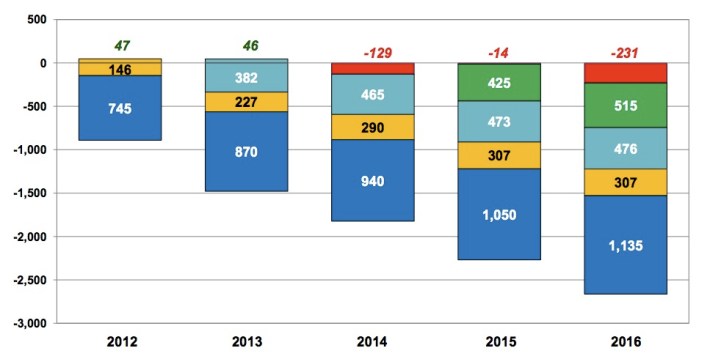
Here's how the MTA broke down the evolution of its finances since February:
The July Plan includes some significant favorable changes that have resulted in a net favorable re-estimate:
- Favorable 2011 results increased the cash carry-over;
- Higher ridership related revenues;
- Lower energy prices;
- Debt service savings; and
- Mid-year release of a portion of the general reserve.
Offsetting those results were some adverse changes:
- 2012 real estate transaction tax receipts running under budget;
- Unfavorable arbitration ruling with the Amalgamated Transit Union;
- Higher OPEB estimates will result in increased contributions to the GASB fund;
- Higher pension costs (lower rate of return assumption); and
- Higher worker’s compensation costs (increased number of claims).
The reduced energy costs alone saved the MTA $50 million for 2013, while soaring transit ridership meant fare revenues $29 million above expectations. Continued attempts to reduce paratransit costs by encouraging some disabled riders to use the subway, bus, or a taxi are expected to save $40 million next year, with far more significant savings in years to come.
Those savings are partially offset by the MTA needing to contribute more to a fund for retiree health care ($22 million more than expected) and by disappointing returns from the real estate tax ($26.5 million under expectations).
These revisions aren't indicative of the most important trends driving the MTA budget overall -- debt service is the fastest-growing piece of the MTA's budget -- just the short-term changes that freed up a little bit of room for service restorations. For a real return to fiscal health, the MTA needs stable, dedicated revenue streams and a capital plan that doesn't overload the transit system with debt.